The evolution of planting paper manufacturing techniques is a fascinating subject, revealing how innovation and ecology can come together to create a unique product. From its traditional beginnings to the most sophisticated modern processes, planter paper has gone through various phases of improvement. These technological advances have made it possible not only to increase the quality of the finished product, but also to optimise its environmental impact. In this article, we will explore the main stages in this evolution, highlighting the major innovations and their influence on current planted paper production.
First manufacturing techniques
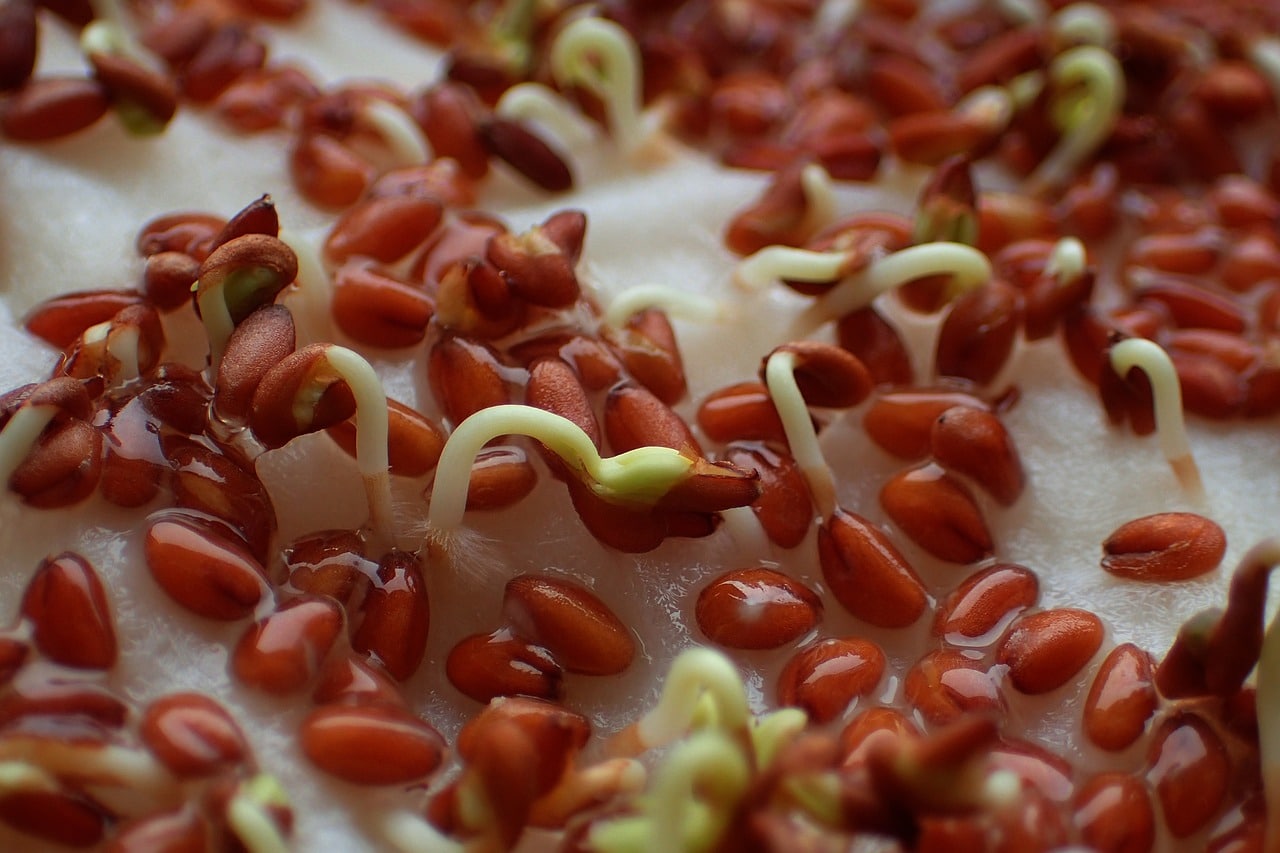

Craft origins
Originally, planting paper was made purely by hand. The first craftsmen used rudimentary methods, often handed down from generation to generation. Plant fibres such as linen, cotton and hemp were the raw materials of choice. These fibres were first soaked and beaten to create a homogenous pulp. This pulp was then spread out on a sieve and left to dry in the sun, forming sheets of paper.
Adding seeds
The idea of incorporating seeds into paper came from observing natural cycles. Craftsmen began to incorporate seeds directly into the pulp before drying. Although this technique was simple, it posed major challenges: the seeds had to be kept intact during the manufacturing process to ensure that they did not germinate prematurely. The ingenuity of the first manufacturers enabled them to overcome these obstacles by adjusting the drying conditions and using particularly resistant seeds.
Drying and preservation techniques
Drying the planting paper was crucial to preserving the seeds. Natural methods, such as air-drying, were commonly used. However, this technique required a favourable climate and a great deal of time. To overcome these constraints, more controlled drying processes were developed, making it possible to produce planting paper in larger quantities while guaranteeing the viability of the seeds.
Preparation and formation of the pulp
Before moving on to drying, a crucial stage was the preparation of the pulp. The plant fibres were first sorted and cleaned to remove impurities. They were then ground in water to form a fine pulp. This maceration stage allowed the fibres to bind together, forming a solid, flexible matrix. The seeds were added at this stage, ensuring that they were evenly distributed so that each sheet of paper contained a sufficient number of seeds.
The challenges of small-scale production
Artisanal production of planter paper posed a number of challenges. Climatic variations could affect the quality of the paper, with drying becoming irregular in the event of rain or high humidity. In addition, the quantity of paper produced was limited by the time and resources available. Despite these constraints, the craftsmen managed to create a unique product, appreciated for its originality and ecological potential.
Technical developments: industrial innovations
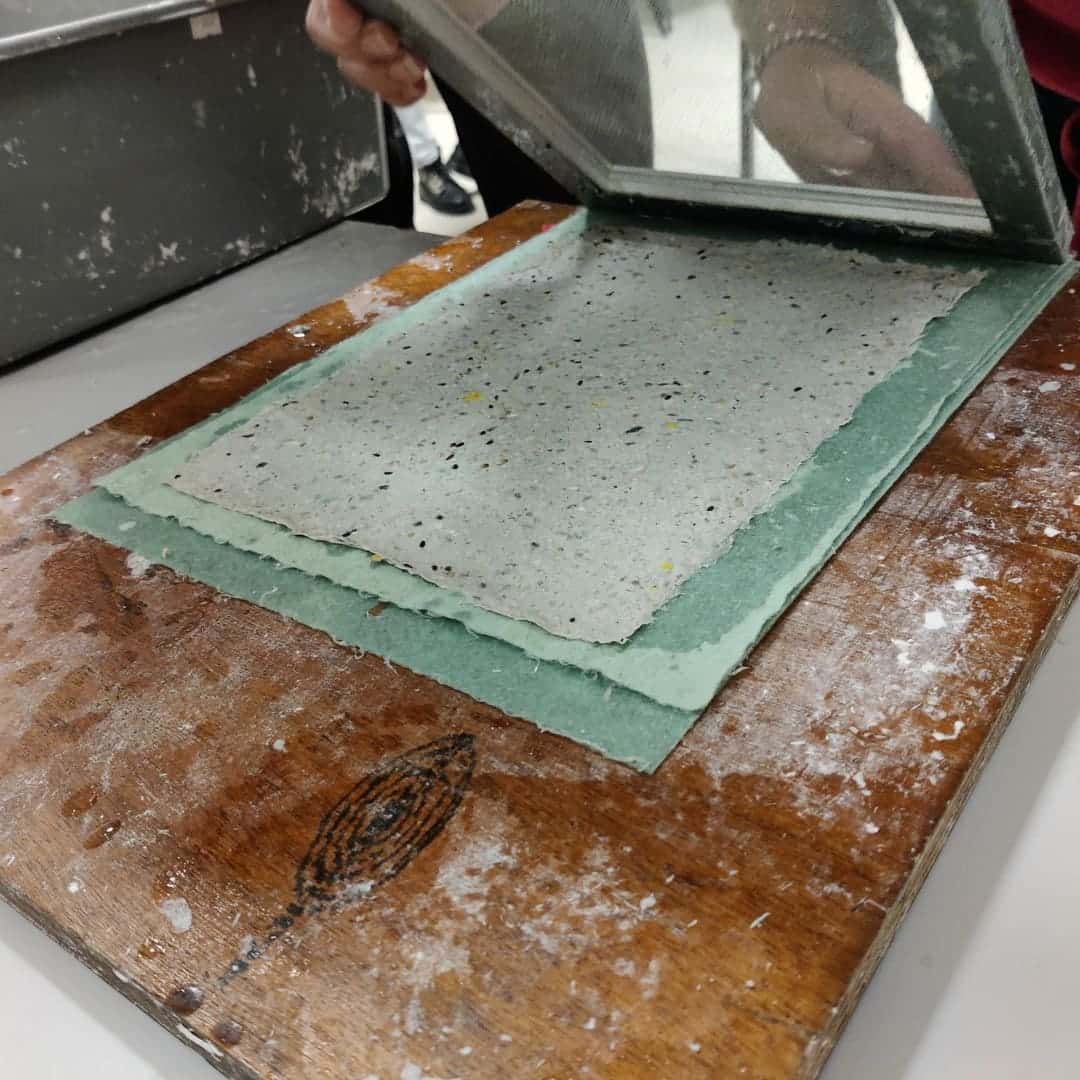

Industrialisation of the process
With the growing demand for environmentally-friendly products, planting paper production techniques have been modernised. Industrialisation has standardised production and improved the quality of the finished product. Plant fibres are now processed in special machines that allow precise control of the consistency of the pulp. This ensures an even distribution of the seeds and a more regular paper texture.
Advanced pulping machines
Modern pulping machines are equipped with advanced technologies that enable plant fibres to be processed more efficiently. These machines can produce an extremely fine pulp, which facilitates the integration of the seeds and improves the quality of the paper. What's more, this equipment allows fibres to be recycled, reducing waste and the ecological footprint of the manufacturing process. Today's pulping systems use mechanical and chemical processes to optimise fibre decomposition and ensure perfect pulp homogeneity. This technological advance has revolutionised the production of planter paper, making the process faster and more reliable.
Modern drying techniques
Drying, once a slow process dependent on climatic conditions, is now achieved using sophisticated equipment. Industrial dryers precisely control temperature and humidity, guaranteeing rapid and uniform drying. This control of drying conditions ensures that the seeds remain viable and that the paper retains its germinative properties. Modern dryers use techniques such as convection drying, where hot air is blown over the paper, or infrared drying, which allows faster, more efficient drying without compromising the quality of the seeds.
Standardisation and quality control
Industrialisation has also introduced rigorous quality control procedures. Each batch of planting paper undergoes tests to check the viability of the seeds and the quality of the paper. These tests include controlled germination to ensure that the seeds are still active after the manufacturing process. In addition, regular checks on the texture, thickness and strength of the paper ensure that the finished product meets the high standards expected by consumers.
Innovations in production
Industrialisation has made it possible to introduce new production methods, such as the use of dies to create specific patterns or shapes in the paper. This has opened up new possibilities for the design and customisation of planting paper, making the product more attractive to a variety of markets. In addition, innovations such as adding nutrients to the pulp to encourage plant growth once the paper has been planted have added further value to the product.
Chez Parsemains
Unlike standardised industrial processes, at Parsemains, each sheet of seeded paper is made entirely by hand, with particular care taken at every stage. From pulping the fibres to seeding and drying, everything is done by hand, without the use of automated machines. This traditional method guarantees total control over the quality of the paper and the viability of the seeds. Our unique know-how enables us to achieve an authentic result, with a unique texture and a meticulous finish. Parsemains is currently the only company in France to manufacture hand-seeded paper, making our production a truly local, ethical and sustainable alternative.
Sustainable approaches and recent innovations
Use of recycled materials
One of the most significant advances in the development of planter paper manufacturing techniques is the use of recycled materials. By recovering used paper and transforming it into new pulp, manufacturers reduce the consumption of natural resources and cut down on waste. This ecological approach is part of a sustainable development approach, making it possible to create a product that is both innovative and environmentally friendly. Recycled paper is carefully collected and sorted to ensure the purity of the pulp, avoiding any contamination that could harm the quality of the paper or the viability of the seeds.
Integration of new seed varieties
Innovation is not limited to manufacturing techniques, but also affects the types of seeds used. Producers of planting paper are experimenting with a wide variety of seeds, from wild flowers to aromatic herbs and even vegetables. This diversity means they can offer products suited to different climates and soils, increasing the chances of successful planting. In addition, some seeds are chosen for their specific properties, such as their ability to attract pollinators or enrich the soil. Current research is focusing on identifying seeds that not only germinate easily, but also provide ecological benefits such as nitrogen fixation or drought resistance.
Innovations in packaging and distribution
Technological advances have also affected the logistical and distribution aspects of planting paper. Packaging is now designed to be as environmentally friendly as the product it contains. Biodegradable inks and recyclable materials are used to minimise environmental impact. In addition, distribution networks have been modernised, enabling faster and more efficient delivery while reducing the carbon footprint. Innovations in the supply chain include optimised transport methods and partnerships with logistics companies committed to sustainable practices.
Marketing techniques and awareness-raising
The promotion of planting paper has also benefited from recent innovations. Marketing campaigns highlight the ecological and educational aspects of the product, making consumers aware of the benefits of planting paper instead of throwing it away. Manufacturers are using digital platforms to reach a wider audience and encourage online purchases, thereby reducing the need for physical sales outlets and lowering the overall ecological footprint. In addition, educational initiatives are being put in place to teach users how to plant and maintain their seeded paper, maximising the chances of successful planting.
The evolution of planter paper manufacturing techniques bears witness to the industry's ability to innovate while respecting the environment. From traditional methods to sophisticated industrial processes, each stage has contributed to improving the quality and durability of this unique product. Recent advances, particularly in recycling and seed diversity, show that planting paper still has a bright future ahead of it. By continuing to adopt sustainable and innovative approaches, this industry can not only meet the growing demand for environmentally-friendly products, but also play an active role in preserving our planet.
The future of plantable paper looks promising, with many opportunities for new innovations. Current research is focusing on the creation of even more effective papers, incorporating micro-organisms beneficial to the soil or combinations of seeds specially selected for their synergy. What's more, the expansion of this product into new markets and applications could open up unprecedented horizons, making planting paper a key element in the transition to a greener, more sustainable economy.
In short, planting paper embodies the perfect alliance between tradition and modernity, nature and technology. Its technical evolution reflects a constant desire to minimise environmental impact while offering a useful and innovative product. As techniques continue to improve, it is certain that planting paper will continue to play an important role in promoting ecological and sustainable practices, while inspiring new generations to take care of our planet.


